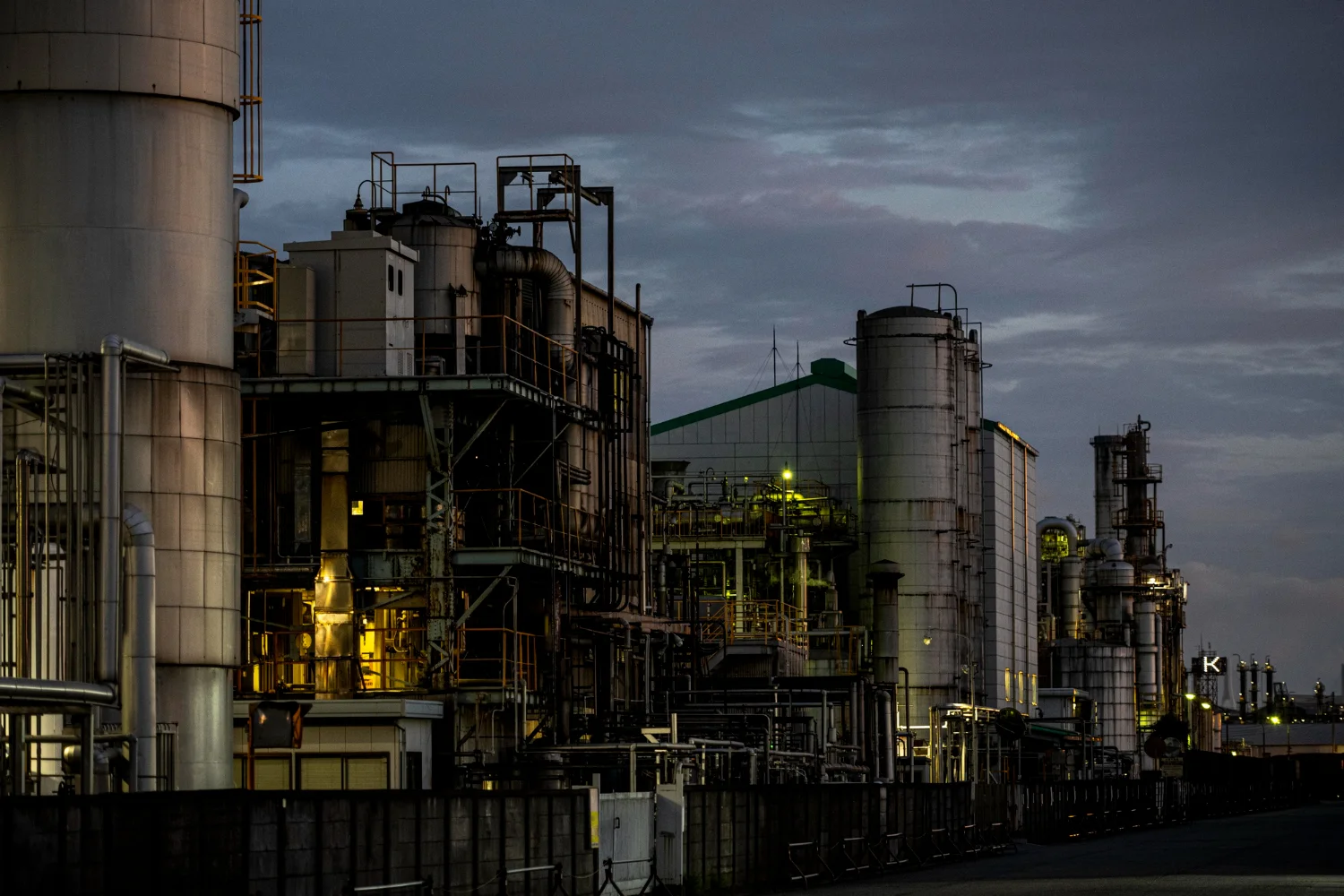
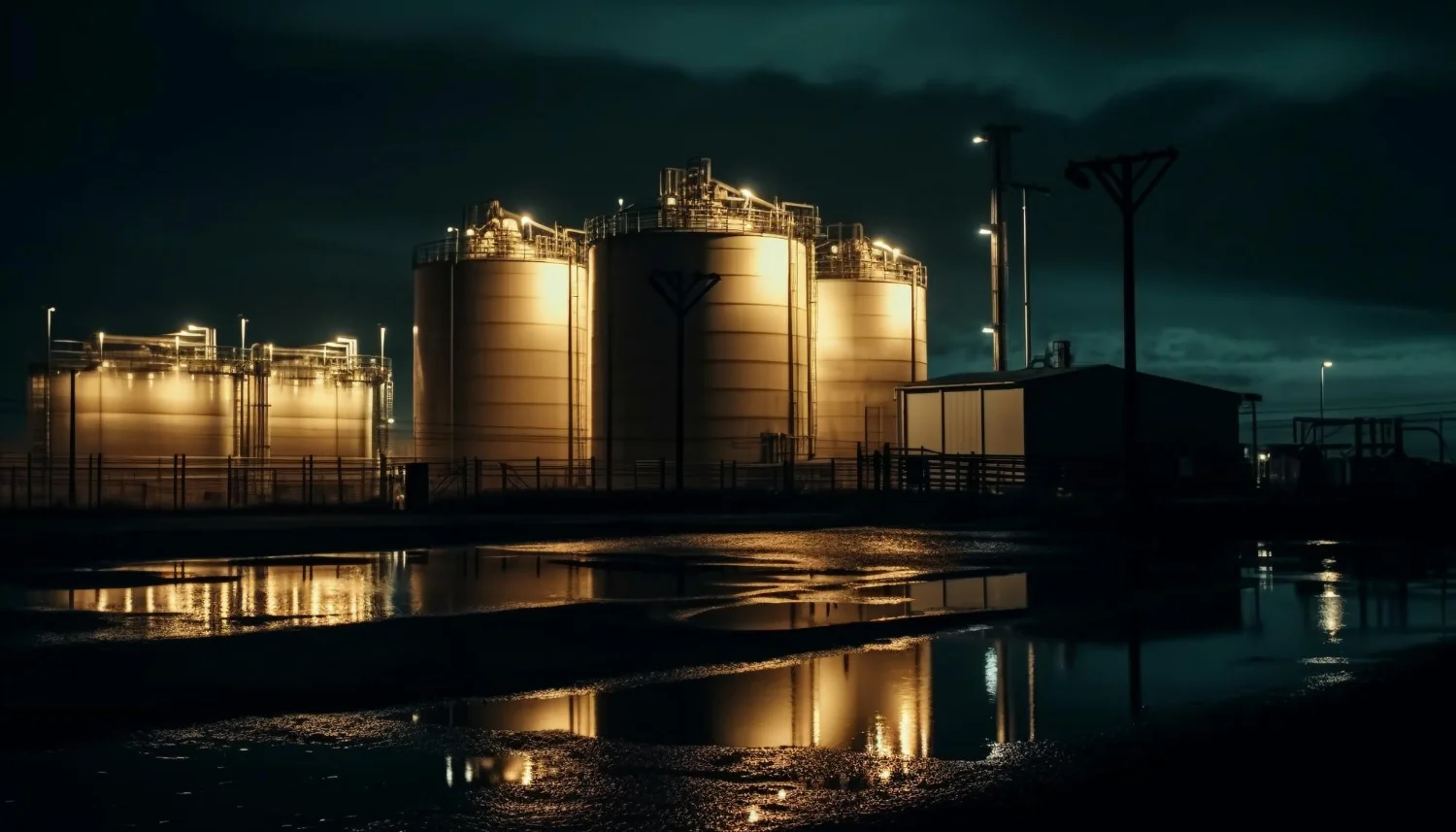
Petroleum Coke, commonly known as Petcoke, is a byproduct of the oil refining process that has become a vital energy source for many industries. Its affordability, high calorific value, and wide range of applications make it a preferred choice for heavy industries across the globe.
1. What is Petroleum Coke (Petcoke)?
Petcoke is produced during the refining of crude oil, where residual oil is heated to produce lighter fuels like gasoline and diesel. The leftover material is converted into solid carbon-rich fuel, known as petroleum coke.
There are two main types:
- Fuel-Grade Petcoke – Widely used in power plants, cement kilns, and boilers.
- Calcined Petcoke – Primarily used in the aluminum, steel, and chemical industries due to its purity and higher carbon content.
2. Key Benefits of Using Petcoke
- High Calorific Value – Generates more heat per unit compared to coal.
- Cost-Effective – Cheaper than most conventional fuels, reducing operational expenses.
- Reliable Supply – Abundant production ensures steady availability in global markets.
- Versatile Applications – Can be used in both energy generation and as a raw material in industrial processes.
3. Industrial Uses of Petcoke
- Cement Industry – Acts as a primary fuel in cement kilns due to its high heat output.
- Power Generation – Used in industrial boilers and power plants for electricity production.
- Steel & Aluminum Production – Calcined petcoke is used as a carbon source in smelting and refining.
- Chemical Industry – Plays a role in manufacturing fertilizers, paints, and other carbon-based products.
4. Environmental Considerations
While petcoke is efficient and economical, it has higher carbon content compared to coal. Industries are adopting advanced technologies and emission control systems to balance cost benefits with environmental responsibility.
Conclusion
Petroleum coke is more than just a refinery byproduct—it is a powerful, cost-effective, and versatile fuel that drives global industries. From cement and steel to power generation, petcoke continues to play a crucial role in meeting energy demands worldwide.